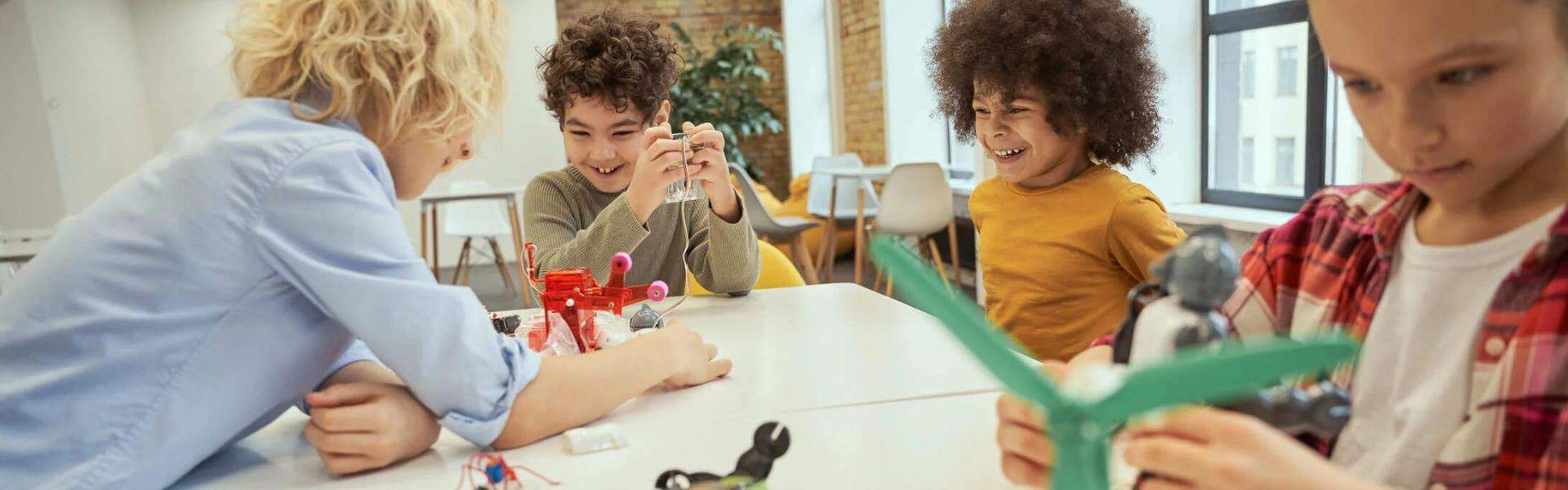
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, various teaching methodologies have been explored to cater to the diverse professional learning communities and styles of students. One such approach gaining traction is kinesthetic learning. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of kinesthetic learning, its significance in educational settings, and the impact it can have on student engagement and academic success.
Understanding Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic learning, often referred to as tactile learning, is a learning style that involves physical activity and hands-on experiences to comprehend and retain information. Individuals who thrive in this learning environment are commonly known as kinesthetic learners. These students benefit significantly from incorporating movement, touch, and physical engagement into their learning experiences.
Principles of Kinesthetic Learning:
- Active Participation: Kinesthetic learners thrive on actively participating in the learning process. Whether it’s through experiments, simulations, or interactive activities, these students benefit from being physically involved in their education.
- Movement Integration: Movement plays a pivotal role in kinesthetic learning. Incorporating activities that involve gestures, role-playing, or even simple exercises can enhance understanding and retention for these learners.
- Hands-On Experience: The hands-on approach is a hallmark of kinesthetic learning. Providing tangible objects, interactive projects, and real-world applications fosters a deeper understanding of concepts.
Benefits of Kinesthetic Learning in Schools:
- Improved Retention and Understanding: Kinesthetic learning has been shown to enhance information retention and understanding. By engaging multiple senses, students can grasp and retain complex concepts more effectively.
- Increased Motivation: The active and dynamic nature of kinesthetic learning tends to boost students’ motivation and enthusiasm for learning. The interactive elements create an engaging environment that captures students’ interest.
- Catering to Diverse Learning Styles: Every student learns differently, and kinesthetic learning provides a valuable alternative for those who may not excel in traditional classroom settings. By acknowledging and accommodating diverse learning styles, schools can create a more inclusive educational environment.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Kinesthetic activities often involve critical thinking and problem-solving. Students learn to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations, honing their analytical skills and creative thinking abilities.
Applications of Kinesthetic Learning in Education:
- Science and Mathematics: Kinesthetic learning finds natural alignment in subjects like science and mathematics. Through experiments, simulations, and hands-on projects, students can better understand abstract concepts and theories.
- Language Arts: Even in language arts, kinesthetic learning can be incorporated. Acting out scenes from literature, participating in interactive storytelling, and using physical props can enhance language comprehension and communication skills.
- History and Social Studies: Historical events and societal structures can come alive through kinesthetic activities. Role-playing, reenactments, and interactive projects help students connect with the past on a deeper level.
- Physical Education Integration: Integrating kinesthetic learning into physical education classes creates a holistic approach to education. This synergistic combination not only promotes physical health but also reinforces academic concepts through movement.
Characteristics of Kinesthetic Learners
Identifying kinesthetic learners can be crucial for educators aiming to create inclusive and effective learning environments. Kinesthetic learners typically exhibit the following characteristics:
- Hands-On Approach: Kinesthetic learners prefer activities that involve hands-on experiences, such as experiments, projects, or interactive simulations.
- Movement: These learners often struggle with prolonged periods of sitting and benefit from incorporating movement into their learning, such as pacing while studying or using tools like stress balls.
- Spatial Awareness: Kinesthetic learners have a heightened sense of spatial awareness and tend to understand concepts better when they can visualize and manipulate objects.
- Physical Expression: They may use physical expressions, gestures, or body language to communicate or understand concepts better.
The Importance of Kinesthetic Learning in Education
Now, let’s explore the significance of kinesthetic learning in the context of schools and education.
- Enhanced Engagement:Kinesthetic learning actively involves students’ engagement in the learning process, fostering a higher level of engagement. By incorporating movement and hands-on activities, educators can capture the attention of kinesthetic learners and make the learning experience more enjoyable and memorable.
- Improved Retention and Understanding:Research suggests that physical movement and touch can enhance memory retention. Kinesthetic learners often struggle to grasp abstract concepts in a traditional classroom setting. However, when these concepts are reinforced through physical activities, students are more likely to understand and remember the material.
- Customized Learning:Kinesthetic learning allows for a more personalized and flexible approach to education. Teachers can incorporate a variety of activities and projects that cater to different learning styles, ensuring that kinesthetic learners have opportunities to thrive alongside their auditory and visual counterparts.
- Developing Life Skills:Beyond academic benefits, kinesthetic learning helps students develop essential life skills such as problem-solving, teamwork, and critical thinking. Collaborative projects and interactive activities promote the development of these skills in a practical, real-world context.
Practical Strategies for Implementing Kinesthetic Learning
Educators can employ various strategies to integrate kinesthetic learning into their classrooms management effectively:
- Hands-On Activities:Incorporate hands-on activities, experiments, and simulations that allow students to physically engage with the subject matter. For example, in a science class, students could conduct simple experiments to understand scientific principles.
- Interactive Technology:Utilize interactive technology, such as educational apps and simulations, that encourage movement and physical interaction. This approach combines the benefits of technology with the kinesthetic learning style.
- Flexible Seating Arrangements:Create a classroom environment with flexible seating arrangements that accommodate movement. This can include standing desks, stability balls, or even allowing students to choose their preferred seating to cater to their individual needs.
- Role-Playing and Drama:Incorporate role-playing and drama activities to make learning more interactive. This not only engages kinesthetic learners but also promotes creativity and communication skills.
- Incorporate Movement Breaks:Recognize the importance of movement breaks during class. Short breaks for stretching or quick physical activities can re-energize students and enhance their focus.
Challenges and Considerations
While kinesthetic learning has numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge potential challenges and considerations:
- Resource Constraints:Implementing kinesthetic learning may require additional resources such as materials for hands-on activities or technology tools. Schools need to allocate resources effectively to ensure all students have access to these opportunities.
- Assessment Methods:Traditional assessment methods may need adaptation to evaluate the understanding and performance of kinesthetic learners. Teachers should explore diverse assessment strategies that align with the hands-on nature of kinesthetic learning.
- Classroom Management:Introducing movement and hands-on activities may pose challenges in terms of classroom management. Establish clear guidelines and expectations to ensure a structured and productive learning environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kinesthetic learning stands as a powerful tool in the educational landscape, offering a unique and effective approach to cater to the diverse learning styles of students. By acknowledging the importance of physical engagement, educators can create dynamic and inclusive classrooms that foster enhanced engagement, improved retention, and the development of crucial life skills.
As the educational paradigm continues to evolve, embracing kinesthetic learning represents a step towards creating enriching and impactful learning experiences that empower students for success in both academic and real-world scenarios.